It’s crucial to choose right soil amendments when it comes to creating an ideal growing environment for your plants. Two of the most popular options are Vermiculite and Perlite. Although they may seem similar at first glance, there are differences between Perlite and Vermiculite. Whether you plan to start seeds, propagate cuttings, or optimize your potting mix, it’s important to know what Vermiculite and Perlite are used for in soil.
In this article, we’ll delve into the unique characteristics of each amendment, their specific uses in gardening, and how to choose the right one for your plants. With this knowledge, you can enhance your gardening practices and ensure your plants thrive.
What Is Perlite?
Perlite is a lightweight, volcanic glass that is widely used in plant propagation. It provides the ideal environment for healthy root growth and overall plant development. Here is how it can benefit your plant growth:

What Is Perlite?
- Improved Drainage: Perlite enhances soil drainage, preventing water from accumulating around plant roots. This is essential for preventing root rot, especially in cuttings and seedlings more susceptible to overwatering.
- Aeration: Its porous nature promotes excellent airflow within the growing medium, ensuring that roots receive the oxygen they need for healthy growth. This is particularly important during the rooting process.
- Lightweight: Perlite is very light, making it easy to handle and ideal for creating a well-balanced potting mix without adding excessive weight to pots, which is beneficial for hanging baskets or shelves.
- Sterility: Perlite is chemically inert and sterile, reducing the risk of disease and pests during plant propagation. This makes it a safe choice for starting new plants from cuttings or seeds.
- Versatility: It can be used alone or mixed with other growing mediums, such as peat moss or vermiculite, to create a customized soil mix tailored to specific plant needs.
- Rooting Cuttings: When propagating plants from cuttings, using a perlite mix can encourage faster root development due to its retaining moisture while allowing excess water to drain away.
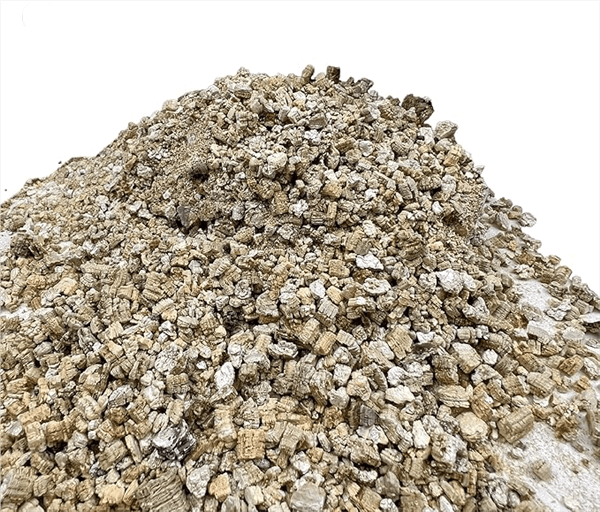
What Is Vermiculite?
Vermiculite is a natural, hydrous silicate mineral that is widely used in plant propagation due to its beneficial properties. In the context of propagation, Vermiculite serves several important functions: it has excellent moisture retention capabilities, allowing it to hold water and nutrients while preventing the soil from becoming waterlogged. This makes it ideal for starting seeds and rooting cuttings, as it provides a consistently moist environment that encourages healthy root development.

What Is Vermiculite?
Additionally, Vermiculite’s lightweight, fluffy texture improves aeration in the growing medium, ensuring that roots receive adequate oxygen. As it is sterile and pH-neutral, it reduces the risk of disease and provides a clean environment for young plants. Overall, Vermiculite is a valuable component in potting mixes and propagation mediums, helping to create optimal conditions for plant growth and development.
Differences between Perlite and Vermiculite
When selecting a growing medium for your plant's growth, you can choose Perlite or Vermiculite. However, Perlite is not the same as Vermiculite. Then you may ask which one you should choose - Perlite or Vermiculite? Don’t worry! Here, we’ll break down the key distinctions between these two soil amendments and how they can impact the health and growth of your beloved flora. From water retention to nutrient availability, understanding the nuances of perlite and vermiculite is crucial for cultivating a thriving garden or lush indoor plant oasis.
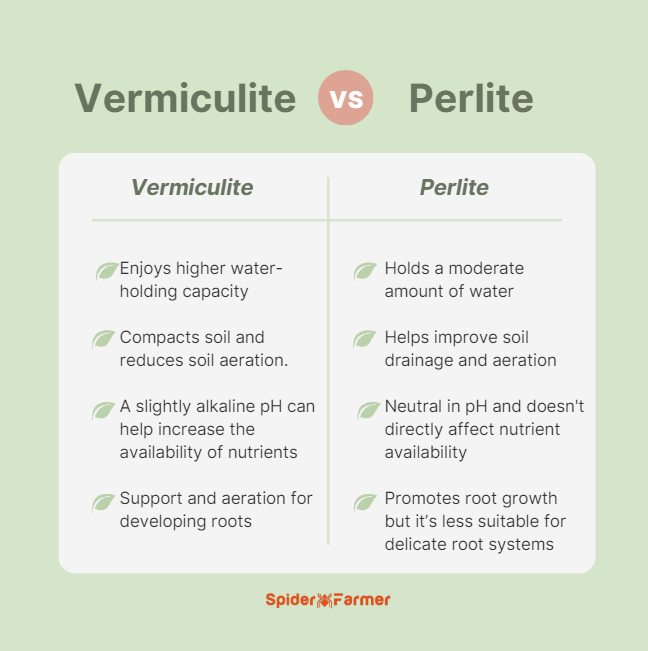
Perlite Vs Vermiculite - Differences between Perlite and Vermiculite
Water Retention
- Vermiculite has a higher water-holding capacity compared to Perlite, which makes iit better suited for plants that prefer moist soil conditions.
- Perlite helps improve drainage and aeration, making it more suitable for plants that prefer well-draining, drier soil.
Soil Aeration
- Vermiculite, while retaining more moisture, can compact over time and reduce soil aeration.
- Perlite is more effective at improving soil aeration and drainage, which is beneficial for plants that are susceptible to root rot or prefer a more oxygenated root zone.
Nutrient Availability
- Vermiculite has a slightly alkaline pH and can help increase the availability of certain nutrients, such as magnesium and calcium, in the soil.
- Perlite is neutral in pH and does not directly affect nutrient availability.
Plant Suitability
- Plants that prefer well-draining, aerated soil, such as succulents, cacti, and some herbs, often perform better with a higher ratio of perlite in the potting mix.
- Plants that require consistently moist soil, such as ferns, some houseplants, and moisture-loving vegetables, may thrive better in a potting mix with a higher proportion of vermiculite.
Rooting and Transplanting
- Perlite’s coarse texture can provide better support and aeration for developing roots, making it beneficial for propagating and transplanting plants.
- Vermiculite’s flaky structure can also aid in root growth, but its higher water-holding capacity may make it less suitable for delicate root systems during transplanting.
Although there are differences between Perlite and Vermiculite, you can use Perlite and Vermiculite together. This can create a well-balanced growing medium that combines the benefits of both. The mix can enhance soil aeration and drainage, thanks to perlite’s lightweight, porous nature, while also improving moisture retention and nutrient availability through Vermiculite’s ability to hold water. Combining these two materials allows you to tailor the growing medium to meet the specific needs of your plants, making it especially useful for those that require both good drainage and consistent moisture.
Where to Find Perlite?
You can find Perlite at various locations, including garden centers, home improvement stores, and nurseries, where it is typically sold in bags alongside other soil amendments and potting mixes. Additionally, many online retailers offer perlite, making it easily accessible for home gardeners and professional growers alike. When purchasing, look for products labeled specifically for horticultural use to ensure quality. It's also common to find perlite in hydroponic supply stores, as it is a popular choice for growing mediums in hydroponic systems.
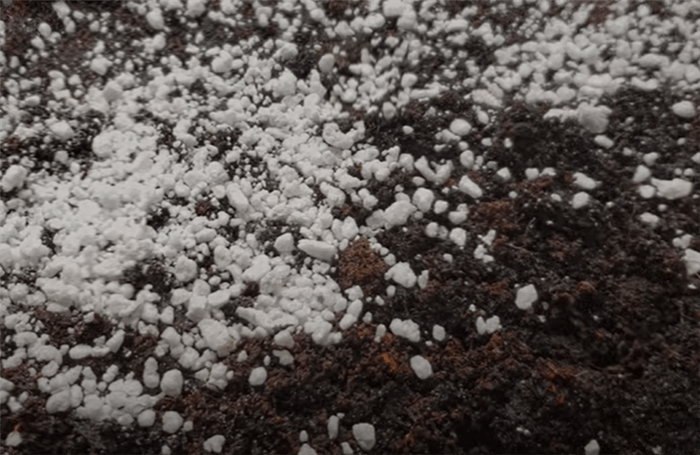
How to Use Perlite?
To effectively use Perlite, start by mixing it into your potting soil to improve drainage and aeration, typically at a ratio of 10-30% Perlite to the total volume of soil, depending on the specific needs of your plants. For seed starting or propagation, you can use pure Perlite or combine it with other materials like vermiculite to create a well-draining, moisture-retentive medium. When potting plants, ensure that Perlite is evenly distributed throughout the soil to prevent clumping, which can impede drainage. Additionally, when using Perlite, it's important to monitor watering closely, as its excellent drainage properties may require more frequent watering than traditional soil mixes. Overall, Perlite is versatile and can be tailored to suit various plant types and growing conditions.

How to Use Perlite?
Where to Find Vermiculite?
You can purchase Vermiculite at various locations, including garden centers, home improvement stores, and nurseries. It is typically available in bags alongside other soil amendments and potting mixes. Many online retailers also offer Vermiculite, making it convenient for both home gardeners and professional growers to find. When buying, look for Vermiculite labeled for horticultural use to ensure quality and suitability for plant cultivation. Additionally, it can often be found at hydroponic supply stores, as it is commonly used in various growing systems.
Table of Contents
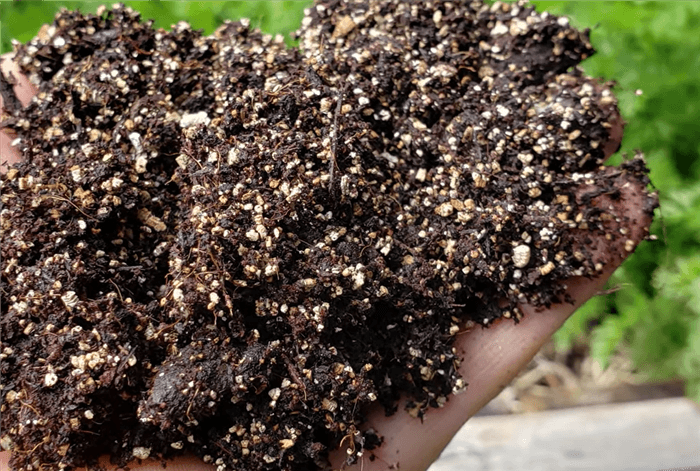
How to Use Vermiculite?
To use Vermiculite effectively, start by incorporating it into your potting mix to enhance moisture retention and aeration, typically at a ratio of 10-50% vermiculite, depending on the specific needs of your plants. For seed starting or propagating cuttings, you can use a mix of equal parts vermiculite and peat moss or combine it with other soil amendments like perlite to create an optimal growing medium that retains moisture while allowing for good drainage. When potting plants, ensure that vermiculite is evenly distributed throughout the mix to prevent compaction, which can restrict root growth. Additionally, vermiculite’s sterile nature helps reduce the risk of disease, making it an excellent choice for nurturing healthy seedlings and new plants. Overall, vermiculite is a valuable tool in gardening that can significantly improve soil structure and plant development.

How to Use Vermiculite?
Conclusion
In the debate between the differences of Vermiculite and Perlite, the choice depends on specific needs. Vermiculite excels in water retention and nutrient availability, making it ideal for moisture-loving plants and seed starting. In contrast, perlite offers superior drainage and aeration, beneficial for plants that require well-drained soil. Ultimately, combining the two can provide a balanced medium, enhancing both moisture retention and aeration, catering to a wider range of plant types. The best choice will depend on the specific requirements of the plants being grown.