When it comes to the world of produce, there might be confusion between the terms “fruit” and “vegetable”, as they are often interchangeably used in culinary contexts. Botanically speaking, fruits and vegetables differ in their development from a flowering plant. A fruit develops from the flower’s ovary and contains the plant’s seeds, while vegetables consist of other edible parts, such as roots, stems, and leaves.
This classification method leads to some surprising results - some vegetables are actually fruits. For example, tomatoes, cucumbers, green beans, okra, olives, pumpkins, sweet corn, sweet peppers, avocados, and zucchini are all fruits.
In this exploration, we’ll uncover what vegetables are really fruits, explain why fruits that people think are vegetables, and reveal the differences between a vegetable and a fruit. This will enhance your culinary creativity and your appreciation for these foods.
Table of Contents
What Vegetables Are Really Fruits?
Several fruits that people think are vegetables are classified as fruits. This is because of their botanical characteristics. In botanical terms, a fruit is the mature ovary of a flowering plant, typically containing seeds. This definition includes many plants we commonly refer to as vegetables, such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and bell peppers, which develop from the flower of the plant and contain seeds within them.
What Vegetables Are Really Fruits?
This classification arises because plants develop their reproductive structures to facilitate seed dispersal, and those structures can often be edible. The culinary distinction, however, is based on flavor and usage, leading to the common misconception that these fruits are vegetables.
In this part, we’ll see what veggies are actually fruits and explain why these “vegetables” are classified as fruits.
Is Tomato a Fruit?
Yes, a tomato is a fruit because it develops from the ovary of a flowering plant and contains seeds. While often used culinarily as a vegetable due to its savory flavor profile, the tomato's biological origin as the mature ovary of the tomato plant firmly places it in the fruit category.

Is Tomato a Fruit?
Is Pepper a Fruit?
Yes, a pepper is a fruit because it develops from the flower of the pepper plant and contains seeds. Although pepper is commonly used as a vegetable in cooking due to its savory flavor, its origins as the mature ovary of the pepper plant firmly places it in the fruit category. This classification follows the scientific definition that fruits are the seed-bearing structures of flowering plants, highlighting a frequent difference between botanical and culinary terms.

Is Pepper a Fruit?
Is Cucumber a Fruit?
Yes, a cucumber is a fruit. This is because it develops from the flower of the cucumber plant and contains seeds. Despite its common usage in salads and savory dishes, which often leads people to think of it as a vegetable, the cucumber's biological origin as the mature ovary of the cucumber plant definitively classifies it as a fruit, according to botanical definitions.

Is Cucumber a Fruit?
Is Squash a Fruit?
Yes, squash is a fruit. Specifically, squash belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family and develops from the flowering part of the carrot, containing seeds within its fleshy structure. This classification applies to all varieties of squash, including zucchini, butternut squash, and acorn squash. The reason for this categorization lies in the biological role of fruit, which is to protect and disperse seeds - a function that squash fulfills. While culinary practices often treat squash as a vegetable due to its savory flavor and common use in dishes, its botanical definition firmly places it in the fruit category.

Is Squash a Fruit?
Is Pumpkin a Fruit?
Yes, pumpkin is classified as a fruit because it develops from the flowering part of the plant and contains seeds. Botanically, fruits are defined as the mature ovary of a flower, which surrounds and protects the seeds. In the case of pumpkins, they form from the fertilized flowers of the pumpkin plant and contain seeds inside their fleshy interior. Although pumpkins are commonly used in savory dishes and often referred to as vegetables in culinary contexts, their botanical classification as a fruit emphasizes the importance of understanding plant reproductive structures and their role in food categorization.

Is Pumpkin a Fruit?
Are Avocados Fruits?
Yes, avocados are fruits rather than veggies. Specifically, avocados are considered large berries, known as drupes, because they have a single seed surrounded by a fleshy pericarp. This botanical classification is based on the fact that fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants, which serve to protect and disperse seeds. Although avocados are often used in savory dishes and salads, their biological characteristics confirm that they fit the definition of a fruit.

Are Avocados Fruits?
Is Okra a Fruit?
Yes, okra is a fruit. This is because it develops from the flower of the okra plant and contains seeds enclosed in a pod. While okra is commonly used in savory dishes and often treated as a vegetable in cooking, its origin as the mature ovary of the okra plant, with the characteristic presence of seeds, unequivocally classifies it as a fruit according to botanical definitions.

Is Okra a Fruit?
Is Eggplant a Fruit?
Eggplant is classified as a fruit, specifically a berry, in botanical terms. This classification arises because it develops from the flower of the plant and contains seeds. While eggplant is commonly used in savory dishes and has a flavor profile associated with vegetables, its biological structure aligns with that of fruits. This distinction illustrates the difference between culinary and botanical classifications, demonstrating how context can influence our understanding of food categorization.

Is Eggplant a Fruit?
Is Carrot a Fruit?
No, a carrot is not a fruit. It’s a root vegetable instead. Fruits are typically defined as the mature ovary of a flowering plant, usually containing seeds, and develop from the flowering part of the plant. Carrots, on the other hand, are the edible taproots of the plant species Daucus carota. They grow underground and are primarily harvested for their nutrient-rich root, which is why they are classified as vegetables rather than fruits.

Is Carrot a Fruit?
Is an Onion a Fruit?
An onion is a vegetable instead of a fruit because it’s the edible bulb of the onion plant and doesn't develop from a flower or contain seeds. Fruits are the mature ovaries of flowering plants and house seeds. Onions, however, are modified underground stems that store nutrients for the plant. Thus, it fits the botanical description of a vegetable, specifically a bulb vegetable.

Is an Onion a Fruit?
What Are the Differences between a Vegetable and Fruit?
The primary difference between a vegetable and a fruit lies in their botanical definitions and culinary uses. Botanically, fruits develop from the flower of a plant and contain seeds, serving the purpose of reproduction; examples include apples, tomatoes, and cucumbers. In contrast, vegetables are other edible parts of the plant, such as roots (carrots), stems (celery), leaves (spinach), and flowers (broccoli), and they do not typically contain seeds. Culinary distinctions also play a role, as fruits are often sweet or used in desserts, while vegetables are generally savory and used in main dishes or sides.
Is Anything with a Seed a Fruit?
Not necessarily. While the presence of seeds is a key characteristic of fruits, it's not the only determining factor. To be classified as a fruit, the structure must also develop from the flower's ovary. Here's a more nuanced explanation:
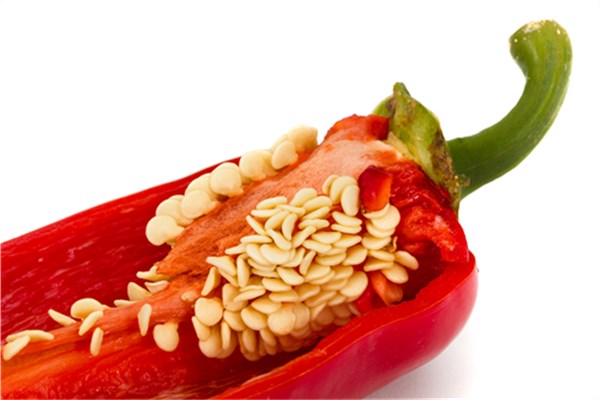

Is Anything with a Seed a Fruit?
Yes, if it develops from the flower's ovary:
If a plant part develops from the ovary of a flowering plant and contains seeds, it is botanically considered a fruit. That’s why tomatoes are a fruit.
No, if it's a seed-bearing structure that doesn't develop from an ovary:
Some seed-bearing structures don’t belong to fruits because they don't originate from a flower's ovary. For example, grains like wheat, rice, and corn are technically fruits, but not in the same way as a tomato or apple. Each kernel is an individual fruit, known as caryopsis or grain, where the ovary wall is fused to the seed.
What Makes a Vegetable a Vegetable?
There are two perspectives to define whether it is a fruit or a vegetable - from either the botanical or the culinary characteristics.

What Makes a Vegetable a Vegetable?
- Botanical Definition: From a botanical perspective, a vegetable is any part of a plant that is not a fruit. This includes the roots, stems, and leaves. More specifically, vegetables are the edible portions of herbaceous plants.
- Culinary Definition: In cooking, vegetables are typically classified based on their savory taste and how they are used in dishes. They are usually eaten as part of the main course or as a side dish.
Vegetables can be further categorized by the plant part that is consumed:
- Root vegetables: Beets, carrots, radishes, sweet potatoes, turnips
- Stem vegetables: Asparagus, kohlrabi
- Leaf and leafstalk vegetables: Brussels sprouts, cabbage, celery, lettuce, rhubarb, spinach
- Bulb vegetables: Garlic, leeks, onions
- Head or flower vegetables: Artichokes, broccoli, cauliflower
- Seed vegetables: Peas and beans
What Vegetables Have Seeds?
Many vegetables contain seeds, as they are the reproductive structures of flowering plants. Some notable examples include:
- Peas: These are often grown for their edible seeds, which are found in pods.
- Beans: Beans, such as kidney beans, black beans, and pinto beans, are actually the seeds of leguminous plants.
- Corn: Each kernel of corn is a seed, and it is classified as a grain but also fits within the vegetable category.
- Spinach: Spinach is a leafy green vegetable that also has seeds. While typically consumed for its tender, nutritious leaves in salads, smoothies, and cooked dishes, spinach is part of the plant's reproductive process.
How to Plant Your Vegetable Fruit at Home?
Growing tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, or squash at home ensures you can enjoy these fruits anytime. It’s easy to plant these vegetable fruits at home with the right care steps:
- Light: Select a sunny location with well-draining soil, as these plants generally need at least six hours of sunlight daily. If you cannot provide enough light, consider using an LED grow light.
- Watering: Assess the needs of your specific plants, as different varieties require varying amounts of moisture. A general rule is to water deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between waterings to promote strong root growth.
- Fertilizer: Amend the soil with compost or other organic matter to improve fertility and drainage.
- Transplanting: When transplanting seedlings, space them according to the plant's mature size, water thoroughly, and provide support such as stakes or cages for vertical gardening.
Conclusion
In this post, you’ve learned what vegetables are really fruits. Normally, we define a fruit and a vegetable from two perspectives - botanical definition and culinary definition. From the botanical side, if the plant develops from the ovary of a flowering plant and contains seeds, it is a fruit. The common list of fruit vegetables includes tomatoes, carrots, squash, pumpkin, cucumbers, and more. Understanding these differences of between a vegetable and a fruit can not only enrich our knowledge of plant biology but also enhance our appreciation for the foods we consume.