Hydroponic gardening has revolutionized the way we grow plants. At the heart of this innovative method, hydroponic fertilizers are crucial in providing plants with essential nutrients. Unlike traditional soil-based gardening, hydroponics relies on nutrient-rich solutions to deliver vital elements directly to the plant roots, which promotes plant growth and health.
This guide will explore the types of hydroponic fertilizers available, how to choose the best one for your plants, and the best practices for using them to achieve healthy, robust growth.
Table of Contents
What Are Different Types of Nutrient Solutions for Hydroponics?
In traditional soil-based gardening, plants obtain nutrients from the soil, but in hydroponic systems, you rely on hydroponic nutrients to provide the essential elements for plant growth. There are several types of nutrient solutions and recipes available. Each solution has a unique composition and benefits.
In this part, we’ll explore various types of nutrient solutions and nutrient solution recipes, finding out the best hydroponic nutrient solutions for your plants.
Types of Nutrient Solutions
- Pre-mixed Nutrient Solutions: The necessary macro and micronutrients have been mixed in proper ratios already. They are convenient for beginners since they only need to dilute the liquid.
- Two-part Nutrient Solutions: These nutrient solutions consist of two separate components - Part A and Part B. Each part contains a different set of nutrients. This is more convenient for growers to control nutrient ratios and customize the liquid based on plant requirements.
- Single-part Nutrient Solutions: They blend of all necessary nutrients in a single bottle. They are easy to use but offer less flexibility compared to another two hydroponic solutions.
Hydroponic Nutrient Solution Recipes
Hydroponic nutrient solution recipes are formulas that specify the amounts of various nutrients to be added to water to create a balanced solution for hydroponic plants. These recipes ensure that plants receive all the essential macronutrients and micronutrients they need.

Hydroponic Nutrients
Here are a few examples of hydroponic nutrient solution recipes:
Modified Sonneveld Solution Recipe
This recipe is suitable for herbs and leafy greens:
- Nitrogen (N): 150 ppm
- Phosphorus (P): 31 ppm
- Potassium (K): 210 ppm
- Calcium (Ca): 90 ppm
- Magnesium (Mg): 24 ppm
- Iron (Fe): 1 ppm
- Manganese (Mn): 0.25 ppm
- Zinc (Zn): 0.13 ppm
- Copper (Cu): 0.023 ppm
- Boron (B): 0.16 ppm
- Molybdenum (Mo): 0.024 ppm
Recipe for Lettuce, Herbs, and Leafy Greens
This recipe is suitable for lettuce, herbs, and leafy greens:
Tank A:
- Calcium nitrate (15-0-0): 184.0 g
- NH4NO3: 14.4 g
- KNO3: 167.3 g
Tank B:
- H4EPO4: 51.5 g
- MgSO4·7H2O: 93.1 g
- MnSO4·4H2O: 72.50 g
- 100μm-Fe (FPA): 3.8 g
- MnMnO4·2H2O: 0.263 g
- ZnSO4·7H2O: 0.279 g
Hydro-FeEd (16-4-17) Recipe
This is a 1-bag solution, use 205 g in 100 gal. of water:
- Tank A: 284 g Calcium nitrate (15-0-0)
- Tank B: 284 g 5-12-26
What Nutrients Are Best for Hydroponics?
Usually, hydroponic fertilizers contain a balanced blend of macro and micronutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, iron, manganese, zinc, copper, boron, and molybdenum. These nutrients are essential for various plant functions, from photosynthesis and root development to fruiting and flowering.

What Nutrients Are Best for Hydroponics?
The best nutrients for hydroponics can provide a balanced mix of essential elements, and you can categorize nutrients into macronutrients and micronutrients.
Here, you’ll see how each nutrient can promote plant growth and yields.
Macronutrients
- Nitrogen (N): Promotes leaf and stem growth and is essential for the production of proteins and enzymes.
- Phosphorus (P): Crucial for root development, flower formation, and energy transfer within cells.
- Potassium (K): Supports overall plant health, disease resistance, and water regulation.
- Calcium (Ca): It’s important for cell wall structure and stability.
- Magnesium (Mg): Involved in chlorophyll production and enzyme activation.
- Sulfur (S): Aids in protein synthesis and enzyme activity.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are required in smaller quantities but are equally important for plant health. They include:
- Iron (Fe): Essential for chlorophyll production and energy transfer within cells.
- Manganese (Mn): Involved in enzyme activation and helps plants withstand stress.
- Zinc (Zn): Needed for the synthesis of growth hormones and root development.
- Copper (Cu): Aids in the formation of lignin, which strengthens cell walls.
- Boron (B): Influences cell division and carbohydrate metabolism.
- Molybdenum (Mo): Necessary for nitrogen fixation and converting nitrate into ammonia.
- Chlorine (Cl): It’s involved in photosynthesis and osmotic regulation.
How to Make Your Own Hydroponic Nutrient Solution?
To make hydroponic nutrients by yourself, you should prepare hydroponic nutrients, water, measuring spoons and cups, mixing containers, a pH meter, pH adjusters, an EC/TDS meter, and a stirring rod.
Then follow the steps below to make your hydroponic nutrient solutions.
- Fill your mixing container with purified water. Measure the pH of the water and adjust it to 5.5-6.5 with pH up or down solutions.
- Divide the nutrients into two parts (A and B). Part A contains calcium and magnesium compounds, while Part B contains phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients. Then measure and add the required amounts of potassium nitrate, phosphoric acid, and other macronutrients from Part B. Stir thoroughly to ensure complete dissolution.
- Measure and add the required amounts of micronutrients (iron, manganese, zinc, copper, boron, molybdenum) to the solution. Then stir thoroughly to ensure complete dissolution.
- Use a pH meter to measure the pH of the solution. Adjust the pH to the optimal range (5.5-6.5) using pH up or pH down solutions. Afterwards, use an EC/TDS meter to measure the electrical conductivity of the solution. Adjust the nutrient concentration if necessary to achieve the desired EC level (typically 1.2-2.0 mS/cm for most plants).
- Ensure the solution is well-mixed to distribute nutrients evenly. Re-measure the pH and EC levels to confirm they are within the desired ranges.
Despite the basic steps, there are some tips for making hydroponic nutrient solutions.
- Use Clean Water: Use purified water, such as reverse osmosis, deionized, or distilled water, to avoid contaminants.
- Measure Accurately: Use a high-precision scale to measure micronutrients, as small amounts are needed.
- Adjust pH Levels: After mixing, test the pH of the solution and adjust it to the optimal range for your plants, typically between 5.5 and 6.5.
- Monitor Nutrient Levels: Regularly check the nutrient levels and adjust based on plant growth and health.
How Often Should You Add Nutrients to Hydroponics?
The frequency of adding nutrients to hydroponics depends on several factors, including the type of system, the size of the reservoir, the growth stage of the plants, and the specific nutrient requirements of the plants being grown.
Generally, it’s recommended to add nutrients to the hydroponic solution every 1 to 2 weeks. During this period, you should regularly monitor the pH and EC levels. When plants consume nutrients and water evaporates, the nutrient concentration can change. For this reason, it’s important to top up the reservoir with water and adjust nutrient levels as needed. Moreover, in the recirculating systems, the nutrient solution may need to be refreshed more frequently, while in non-recirculating systems, nutrients can be added as needed based on plant uptake.
How to Use Hydroponic Nutrients?
After carefully making the hydroponic nutrient solution, introduce it into your hydroponic system. This process is more than just pouring the solution. It also involves properly integrating crucial components into the system.
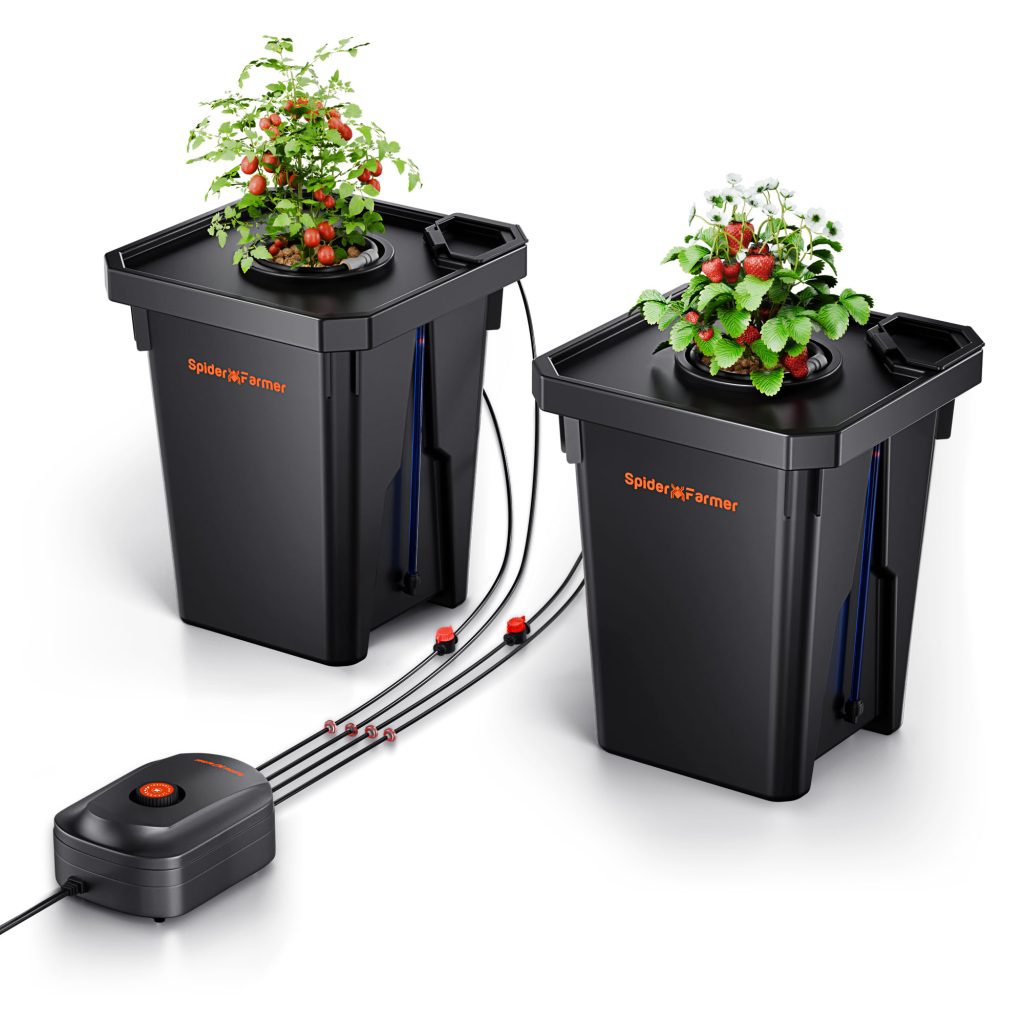
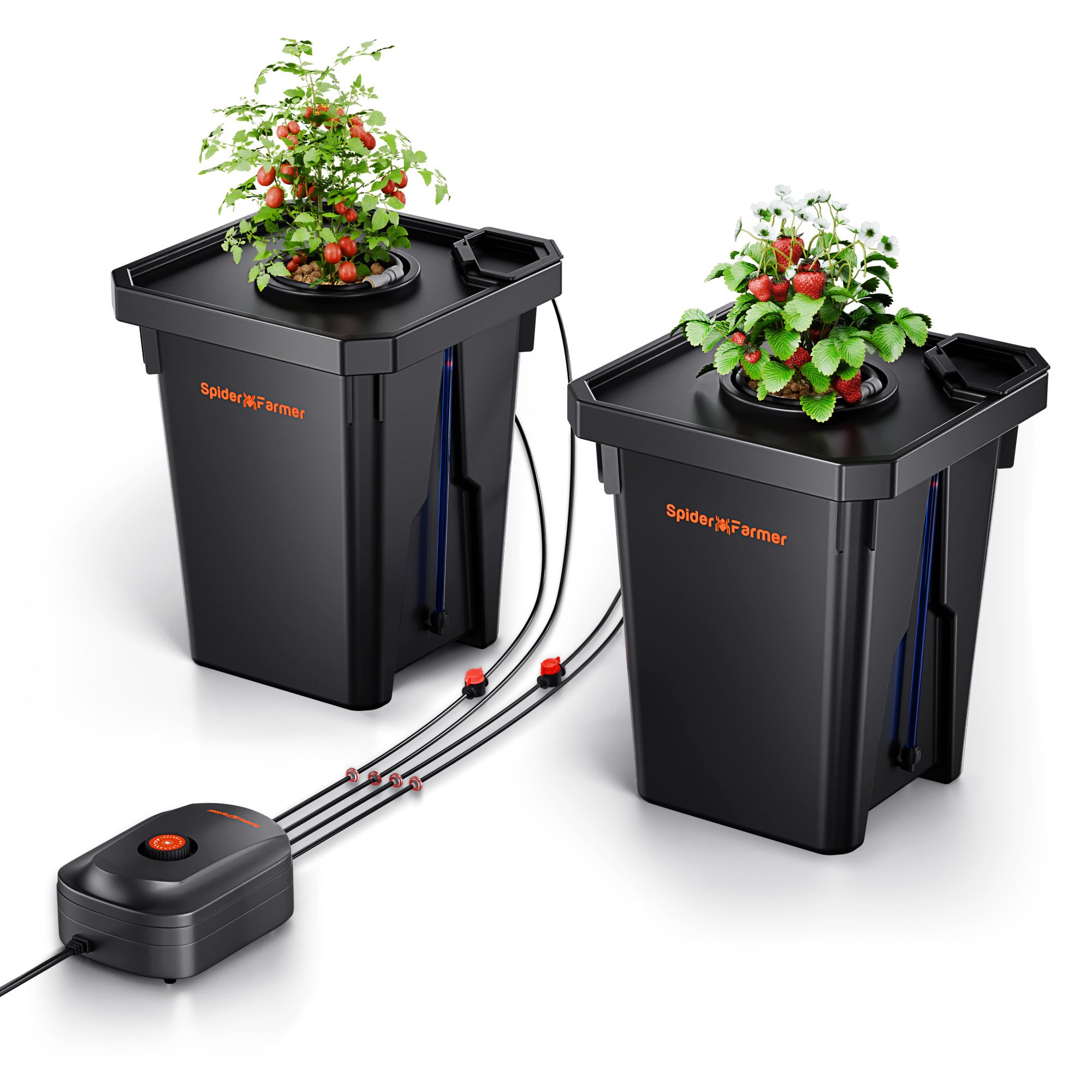
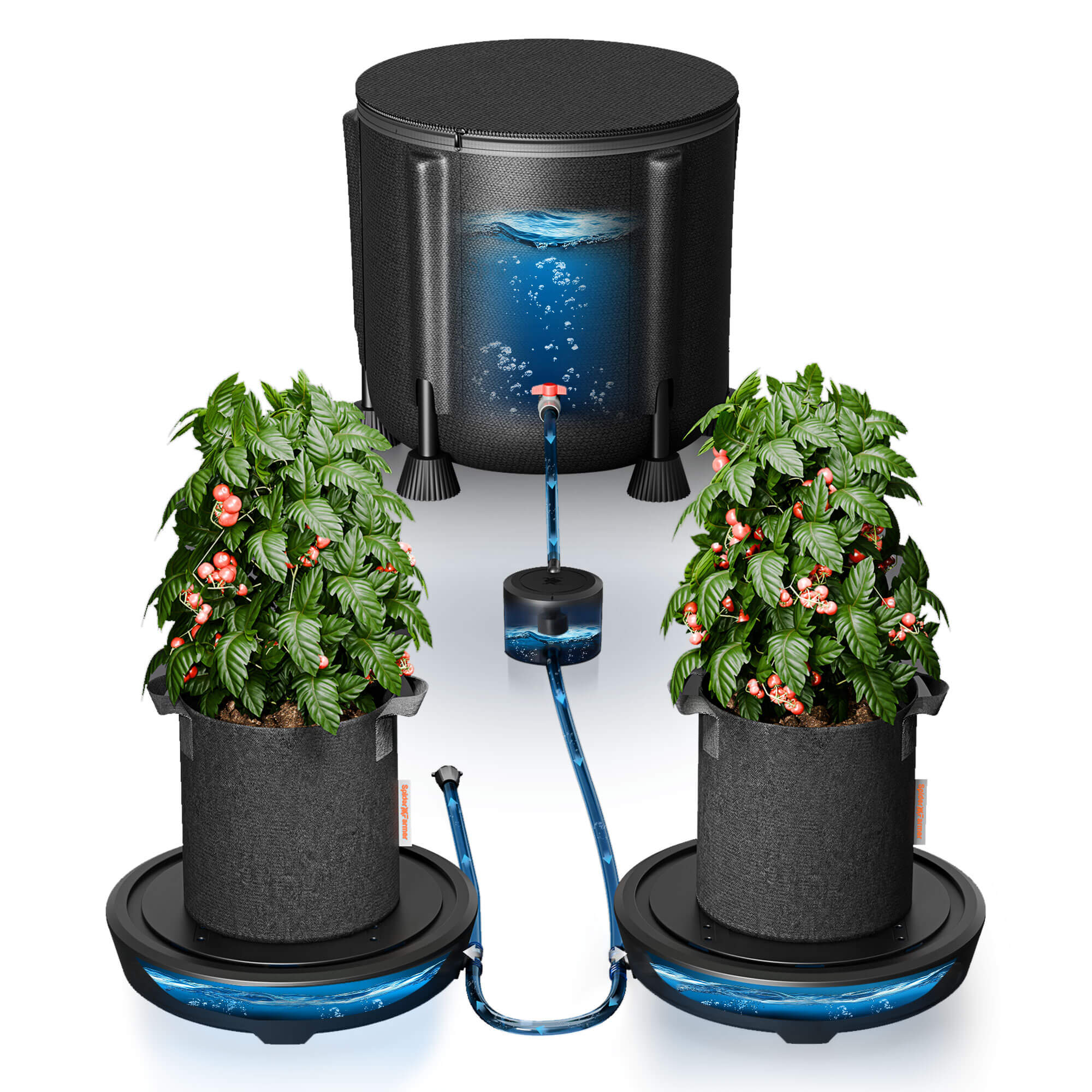
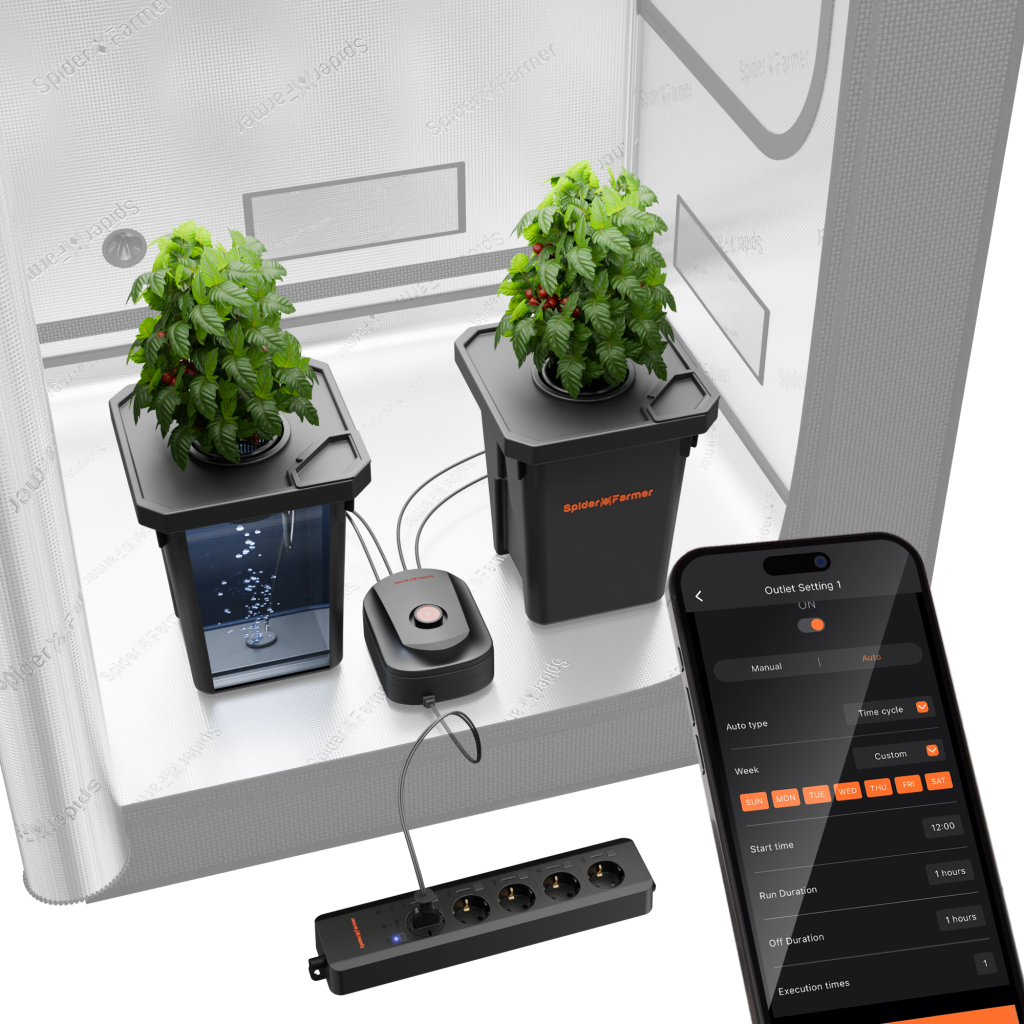
Among the common types of hydroponic systems, Deep Water Culture (DWC) is a popular hydroponic method. In the Spider Farmer DWC Hydroponics Grow System, plant roots are directly submerged in the nutrient solution. They can efficiently take up nutrients from the solution and minimize stress on the plants. To achieve optimal results, it’s crucial to understand how to properly use hydroponic nutrients in a DWC system.
Spider Farmer DWC Hydroponic Growing System with Top Drip Kit, 7-Gallon Deep Water Culture, 2-Bucket Setup, and GGS AC5 Power Strip Kit for Smart Watering Control
In stock
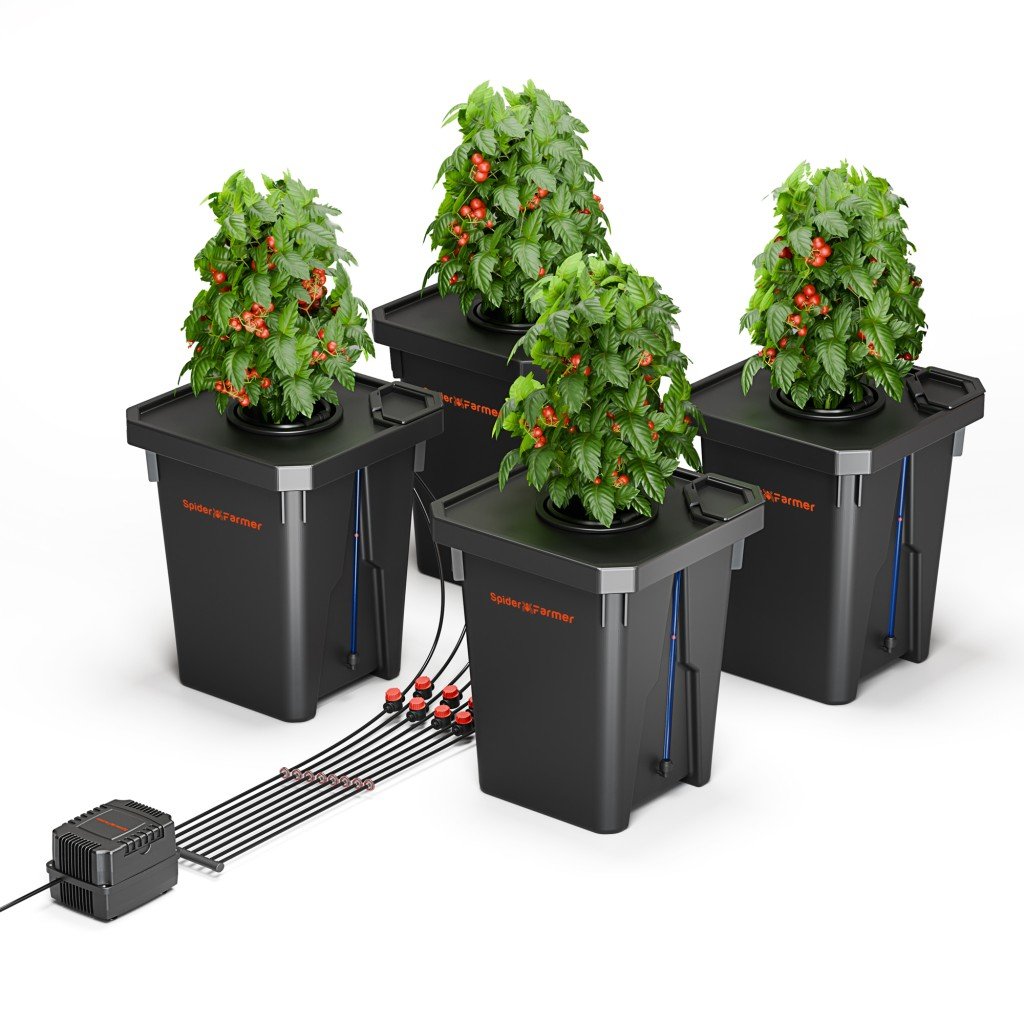
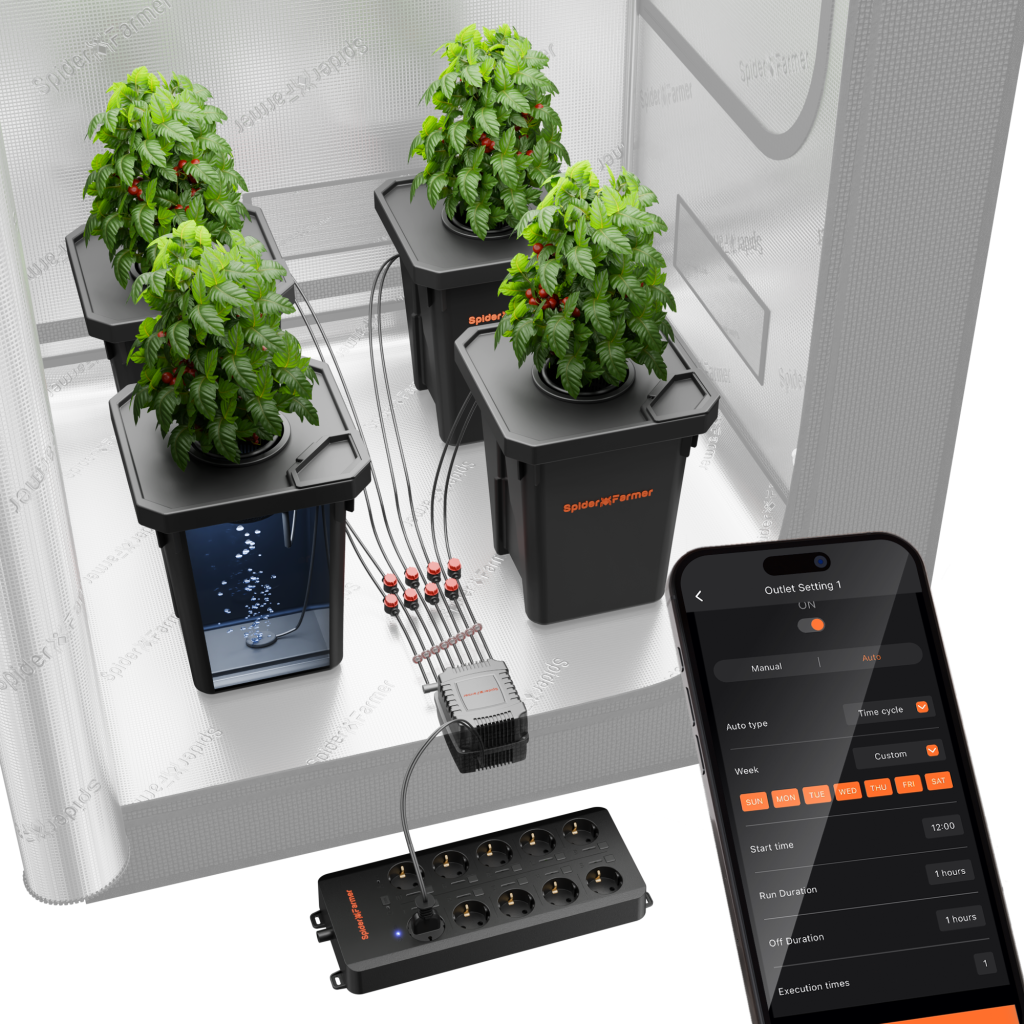
Spider Farmer DWC Hydroponic Growing System with Top Drip Kit, 7-Gallon Deep Water Culture, 4-Bucket Setup, and GGS AC10 Power Strip Kit for Smart Watering Control
In stock
Spider Farmer DWC Hydroponic Growing System with Top Drip Kit, 7-Gallon Deep Water Culture, 4-Bucket Setup, and GGS AC5 Power Strip Kit for Smart Watering Control
In stock
Spider Farmer DWC Hydroponics Grow System 2 Buckets + GGS AC10 Power Strip Kits
In stock
Spider Farmer DWC Hydroponics Grow System with Top Drip Kit 7 Gallon Deep Water Culture 2 Buckets
In stock
Spider Farmer DWC Hydroponics Grow System with Top Drip Kit 7 Gallon Deep Water Culture 4 Buckets
In stock

How to Use Hydroponic Nutrients with DWC System
- Inject the hydroponic nutrient solution into the DWC hydroponic bucket and add purified water to adjust the nutrient solution.
- Place air stones at the bottom of the bucket and connect them to a high-output air pump to oxygenate the water.
- Fill net pots with an inert, porous grow medium like hydroton or rockwool to stabilize the plants. Also, sterilize the grow medium with a hydrogen peroxide solution to eliminate contaminants.
- Position seedlings in the net pots, making sure their roots can make direct contact with the nutrient solution.
- Use a pH meter to maintain the solution's pH between 5.5 and 6.5. Meanwhile, measure the electrical conductivity (EC) to ensure nutrient concentration is within the ideal range for your plants.
- Regularly check the water level and top up with fresh water and nutrients as required. Replace the nutrient solution every 1-2 weeks to prevent imbalances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydroponic fertilizers play a crucial role in the success of hydroponic gardening. By providing a balanced mix of essential macronutrients and micronutrients, these fertilizers ensure that plants receive all the necessary elements for robust growth and high yields.

































-10位排插欧规-1024x1024.png)