Seed germination is a critical stage in the life cycle of a plant, marking the beginning of its journey towards growth and development. Whether you’re an avid gardener, a plant enthusiast, or an aspiring horticulturist, understanding how to succeed in seed germination is essential for nurturing healthy and thriving plants.
By mastering the art of seed germination, you can unlock the potential of various plant species, cultivate a bountiful garden, and witness the miracle of new life taking root. In this blog, we will explore a comprehensive set of strategies, techniques, and tips to help you achieve successful seed germination, empowering you to embark on a rewarding journey of plant propagation and cultivation.
The Importance of Seed Germination
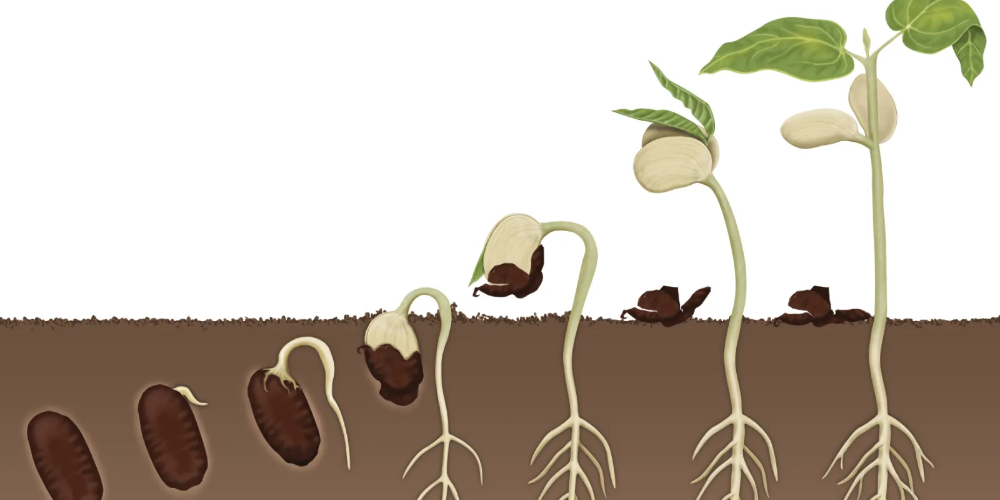
Seed germination is of paramount importance for the subsequent growth and development of plants. It serves as the crucial starting point that sets the stage for a plant’s entire life cycle. During germination, the seed undergoes biochemical changes, triggering metabolic processes and activating the embryonic plant within.
As the seed germinates, essential nutrients stored within the seed are mobilized, providing the energy and resources necessary for initial growth. The emergence of a radicle, the embryonic root, enables the young seedlings to absorb water and essential minerals from the soil. With the establishment of roots, the seedling gains the ability to anchor itself and access further resources for sustained growth.
And successful seed germination determines the vigor and health of the emerging plant, influencing its ability to develop sturdy stems, produce leaves, and eventually flower or bear fruit. In essence, seed germination is the critical foundation that paves the way for the remarkable growth and transformation of a tiny seed into a mature and flourishing plant.
What Are The Basic Requirements Of Seed Germination?
Seed germination relies on several fundamental requirements that must be met to ensure successful growth. These requirements include moisture, temperature, oxygen, and, in some cases, light. Let’s explore each of these factors in more detail, along with specific examples and data.
Moisture is crucial for seed germination as it initiates the imbibition process, where the seed absorbs water and rehydrates its tissues. Different plant seeds have varying moisture requirements, and maintaining proper moisture levels is essential. For instance, lettuce seeds (Lactuca sativa) require moisture levels between 25% and 30% for germination, while tomato seeds require moisture levels of about 50%. Insufficient moisture can lead to failed germination, while excessive moisture can cause seed rot or fungal diseases.
Temperature is another critical factor that influences seed germination. Seeds have specific temperature ranges in which they thrive. For example, basil seeds typically germinate best at temperatures between 20°C and 30°C (68°F and 86°F). In contrast, spinach seeds prefer cooler temperatures of around 10°C to 15°C (50°F to 59°F). Understanding the temperature preferences of different seeds is crucial for providing optimal conditions and promoting successful germination.
Oxygen availability is vital during seed germination. Oxygen is necessary for the respiration process, providing energy for the metabolic activities involved in germination. Without sufficient oxygen, seeds may experience poor germination or even perish.
Light plays a significant role in the germination of certain seeds, influencing their dormancy breakage and subsequent growth. Photoblastic seeds exhibit different light requirements, with some requiring exposure to light for germination (positive photoblastic) and others requiring darkness (negative photoblastic). For instance, lettuce seeds are negatively photoblastic, meaning they require darkness for germination. In contrast, tobacco seeds are positively photoblastic and need exposure to light to initiate germination.
How to Successfully Germinate Seeds Indoors?
- Start with High-Quality Seeds:

High-quality seeds exhibit superior genetic traits, have higher germination rates, and produce healthier and more robust plants. For instance, a study conducted by the University of California, Davis evaluated the germination rates of high-quality vegetable seeds compared to low-quality ones. The results revealed that the high-quality seeds had an average germination rate of 95%, while the low-quality seeds only achieved a rate of 60%. This stark difference demonstrates the significant impact that seed quality can have on successful germination.
Besides, you can choose high quality seeds that are easy to germinate. Here, we recommend some easy-to-germinate seeds for your reference:
- Lettuce: Lettuce seeds are generally easy to germinate, making them ideal for beginners. They typically have high germination rates and quick sprouting times.
- Radish: Radish seeds are known for their rapid germination, often sprouting within a few days. They are reliable and straightforward to grow, making them a popular choice for novice gardeners.
- Marigold: Marigold seeds are relatively easy to germinate and are well-suited for both indoor and outdoor cultivation. They provide vibrant blooms and are a favorite among flower gardeners.
- Basil: Basil seeds germinate readily under favorable conditions. They require warmth and moisture to sprout and are commonly grown as culinary herbs.
- Zinnia: Zinnia seeds are known for their high germination rates and are a popular choice for adding vibrant color to garden beds and containers. They are relatively easy to grow, even for beginners.
- Cucumber: Cucumber seeds typically have high germination rates and are relatively straightforward to grow. They require warm temperatures and adequate moisture for successful germination.
- Sunflower: Sunflower seeds are easy to handle and have a high germination rate. They are a joy to grow and can reach impressive heights, making them a favorite for both children and adults.
- Sweet pea: Sweet pea seeds are known for their reliable germination. They produce beautiful and fragrant flowers and are a popular choice for adding elegance to gardens and bouquets.
- Provide Optimal Environmental Conditions:

Providing optimal environmental conditions is crucial for the successful germination of seeds. Several key factors, including temperature, moisture, light, and air circulation, play significant roles in creating an ideal environment for seed germination.
For example, research conducted at the University of Minnesota examined the effect of temperature on the germination of tomato seeds. The study found that the highest germination rates were achieved when the seeds were exposed to temperatures between 25°C and 30°C (77°F and 86°F).. Additionally, proper moisture management is essential. Seeds require adequate moisture for imbibition and activation of growth processes. However, excessive moisture can lead to fungal diseases and seed rot. Studies have shown that maintaining a moisture content of around 50-70% relative to the seed weight can enhance germination rates for various plant species.
- Prepare the Planting Medium:

Preparing the planting medium is an essential step in promoting successful seed germination. The planting medium, often a combination of soil, compost, and other organic matter, provides the necessary support and nutrients for the seeds to develop into healthy seedlings. What’s more, it is crucial to ensure that the planting medium is loose, well-draining, and rich in organic matter.
Studies have shown that using a well-balanced potting mix with good drainage promotes optimal seed germination rates. For example, research conducted at the University of California, Davis demonstrated that a potting mix composed of equal parts peat moss, perlite and vermiculite yielded superior germination rates for a variety of vegetable seeds.
Additionally, incorporating organic matter such as compost or aged manure enhances the nutrient content of the planting medium, providing essential elements for seedling growth. Prior to sowing the seeds, it is advisable to moisten the planting medium to the appropriate moisture level, ensuring that it is evenly damp but not waterlogged. By preparing a suitable planting medium with the right balance of texture, drainage, and nutrient content, gardeners can provide an ideal foundation for seeds to germinate and thrive.
- Proper Planting Depth and Spacing:

Proper planting depth and spacing are crucial considerations for successful seed germination and subsequent plant growth. Each plant species has specific requirements regarding how deep seeds should be planted and the appropriate spacing between them.
A study found that corn seeds planted at a depth of 1.5 inches had significantly higher germination rates compared to those planted at shallower or deeper depths. This highlights the importance of following recommended planting depths for specific seeds.
- Water Carefully:

Proper watering practices help maintain the ideal moisture levels necessary for seeds to absorb water and activate the germination process. But overwatering can lead to waterlogged soil, which hampers oxygen availability and increases the risk of seed rot or fungal diseases. On the other hand, underwatering can result in insufficient moisture, preventing from germinating seeds indoors or causing stunted growth.
It is recommended to water gently, using a fine mist or a watering can with a narrow spout. This ensures even distribution of water without disturbing the seeds or compacting the soil.
- Provide Adequate Light:

Providing adequate light is crucial for the successful germination of seeds and the subsequent development of healthy seedlings. Light is essential for triggering the process of photosynthesis, which enables plants to produce energy for growth.
When seeds are exposed to sufficient light, it helps them break dormancy and initiates the germination process. While some seeds require darkness for germination, many others benefit from exposure to light. For example, studies have shown that light is crucial for the germination of lettuce seeds. By placing lettuce seeds in a well-lit area or using supplemental artificial lighting, gardeners can enhance germination rates and promote stronger seedling growth. Therefore, it is important to note that different plant species have varying light requirements, and it is essential to research and understand the specific needs of the seeds being sown.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: Can I reuse seed starting trays or pots?
A: Reusing seed starting trays or pots is possible, but it is essential to ensure they are properly cleaned and sanitized before reusing. Cleaning with a mild bleach solution or using new soil for each planting cycle helps minimize the risk of disease transmission and maintains optimal growing conditions.
- Q: How can I protect seedlings from pests?
A: To protect seedlings from pests, it is important to monitor the garden regularly for signs of pest activity. Applying organic pest control methods like using insecticidal soap or introducing beneficial insects can help deter pests. Creating physical barriers such as row covers or using companion planting techniques can also provide protection.
- Q: How deep should I plant the seeds?
A: The planting depth varies depending on the size of the seed. As a general rule, seeds should be planted at a depth that is approximately 2-3 times their diameter. However, some seeds may have specific planting depth requirements, so it is advisable to consult the seed packet for precise instructions.
- Q: Can I start seeds indoors year-round?
A: While starting seeds indoors provides a head start, the timing for indoor seed starting depends on the specific plant and the desired planting time. Most seeds are started indoors a few weeks before the last frost date to allow sufficient time for germination and seedling development.
- Q: How long does it take for a seed to germinate?
A: The time it takes for a seed to germinate varies depending on the plant species and environmental conditions. Some seeds can germinate within a few days, while others may take weeks or even months. Factors such as seed dormancy, temperature, soil moist, and light availability play significant roles in the germination process. For example, lettuce seeds typically germinate within 7 to 10 days, while tomato seeds can take around 5 to 10 days.