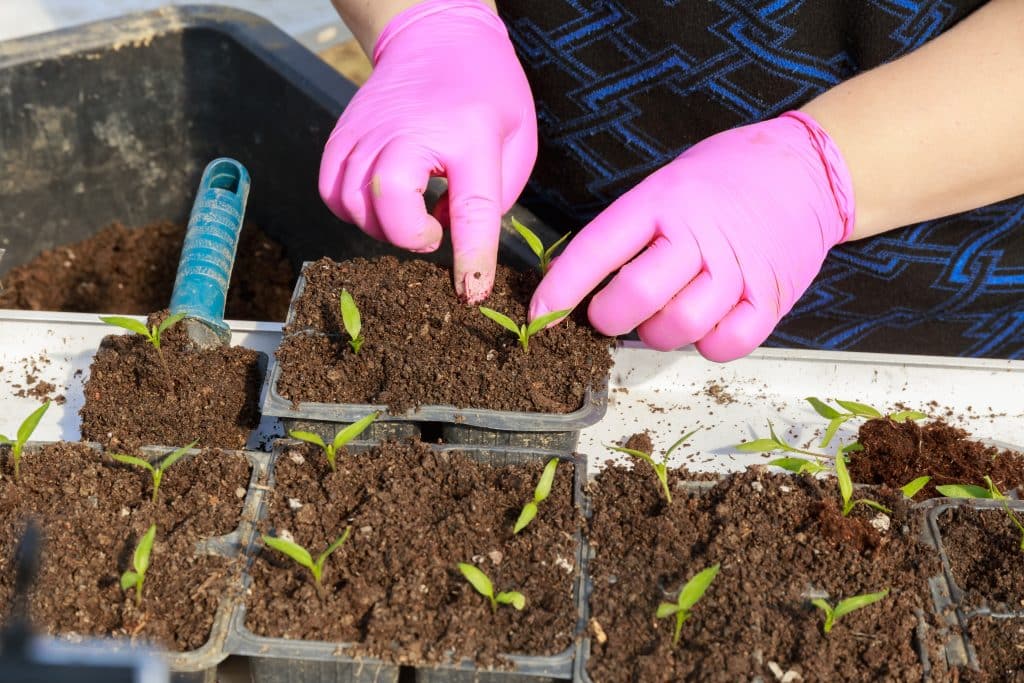
Transplanting seedlings may appear straightforward, but it's a pivotal step in nurturing a thriving garden. When to transplant seedlings is essential to ensure your plants grow robust and healthy. In this article, we'll explore the optimal times for transplanting seedlings, provide invaluable tips, and answer common queries that gardeners often encounter during this essential process.
Table of Contents
What Is the Process of Transplanting
When talking about "transplanting," we mean the act of moving seedlings or small plants from their pots, which could be indoor containers or nursery-bought containers, into the garden soil. This practice is applicable to two main scenarios:
- Small Starter Plants: These are often referred to as "transplants" or "starts" and are typically purchased from a nursery or garden center. Gardeners turn to nurseries for certain vegetables like tomatoes, eggplants, and peppers because these plants can be challenging to start from seeds, or they may take too long to reach a suitable size for outdoor planting.
- Young Plants Started from Home: Some gardeners prefer to start plants from seeds indoors. This approach allows them to kickstart the plant growth stage before the outdoor planting season begins, which is particularly beneficial in northern climates with limited growing seasons. These home-started seedlings are nurtured in containers indoors until they reach an appropriate size for transplanting.
It's worth noting that while transplanting is a common practice, not all vegetables or flowers are suitable for this process. Some plants are best suited for direct sowing in the garden soil, say, lettuce and leafy greens, cucumbers, and other root vegetables.
4 Signs to Know When to Transplant Seedlings
- Emergence of true leaves
The optimal moment to repot your seedlings usually arrives around three weeks after their initial sprouting or when they have grown one to two sets of true leaves, typical during the vegetative stage. It's crucial to relocate them before they start displaying signs of stress, which we'll discuss shortly.
- First leaves are turning yellow and falling off
Cotyledons are the first leaves that emerge when a seed germinates. They are distinct from "true leaves," which appear after the cotyledons. While it's considered normal for cotyledons to become yellow and shed, if this occurs when your seedlings possess only one or two sets of leaves, it serves as a clear signal that it's time to transfer them to larger containers.
What’s more, if the true leaves, which are the second set of leaves to develop after the cotyledons, start changing color to yellow, it's certainly an indication that you should contemplate transplanting.
- The roots are encircling the root ball
When seedlings are cultivated in cell packs, plug trays, or other compact containers, they can quickly reach a point where their roots outgrow the available space. An indicator that signals the need for repotting the seedlings is when you observe roots extending through the drainage holes at the bottom of the containers.
- They're overcrowded
It's advisable to prevent overcrowding your young plants. Some may grow taller than others, impacting the amount of light smaller ones receive. Furthermore, larger plants may monopolize nutrients, hindering the growth of neighboring plants
Seedlings' Specific Needs for Transplanting
Different plants have varying requirements. Here we’ve listed when to transplant seedlings for some common garden favorites:
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a popular choice for many gardeners. Transplant tomato seedlings when they are 5-7 inches tall and have their second set of leaves. Ensure they have been hardened off by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions for a week before transplanting.
Peppers
For pepper plants, transplant seedlings when they are 6-8 weeks old or have at least two sets of true leaves. Similar to tomatoes, hardening off is essential for a smooth transition to the garden.
Herbs
Herbs like basil and parsley can be transplanted once they have 3-4 sets of true leaves and are approximately 4-6 inches tall. Harden them off for a week before transplanting to reduce stress.
Step-by-step Guide on How to Transplant Seedlings
Once you’ve made up your mind to transplant seedlings, here's a step-by-step guide on how to do that effectively:
Materials for Transplanting Seedlings
- Seedlings ready for transplant
- Larger pots or a garden bed
- High-quality potting mix or garden soil
- Small garden trowel or transplanting tool
- Watering can or hose
- Steps to Transplant Seedlings:
How to Transplant Seedlings
Step 1. Prepare the New Containers or Garden Bed
If you're transplanting seedlings into larger pots, ensure they are clean and have drainage holes at the bottom. If transplanting into a garden bed, prepare the soil by removing any weeds or debris.
Step 2. Water the Seedlings
Before transplanting, thoroughly water the seedlings in their current containers. This helps the soil stick together during the transplant and minimizes root disturbance.
Step 3. Choose the Right Timing
The ideal time to transplant is in the late afternoon or on a cloudy day. This reduces stress on the seedlings by minimizing exposure to direct sunlight and heat.
Step 4. Create Holes or Furrows
If transplanting into a garden bed, make holes or furrows in the soil at the appropriate spacing for your seedlings. If using pots, ensure they are filled with fresh potting mix.
Step 5. Remove Seedlings Gently
Carefully remove the seedlings from their current containers. You can do this by lightly squeezing the sides of the container to loosen the soil or by tapping it gently.
Step 6. Plant Seedlings
Place each seedling in a hole or furrow at the same depth as it was in its original container. Space them according to the recommended spacing for the specific plant type.
Step 7. Fill with Soil
Carefully fill the hole or furrow with soil, ensuring there are no air pockets around the roots. Press the soil gently to secure the seedlings.

After transplanting, water the seedlings generously to help settle the soil and reduce transplant shock. Ensure the water reaches the root zone.
FAQs about Transplanting Seedlings
- How big should seedlings be before transplanting?
Seedlings should typically be around 2 to 3 inches tall before they are ready for transplanting. For more precise timing, you can look for other signs of readiness, such as the development of true leaves and a well-established root system.
- What is the best growth stage to transplant seedlings?
The best growth stage for transplanting seedlings is when they have developed their first set of true leaves and are around 2 to 3 inches tall, somewhere around the vegetative stage.
- Why is it better to transplant seedlings in the morning?
Transplanting seedlings in the morning is preferred because the temperatures are usually cooler, and the sun is less intense during this time. Cooler temperatures reduce stress on the seedlings and minimize the risk of heat-related damage.
- What is the best time of day to transplant seedlings?
The best time of day to transplant seedlings is indeed the morning. Transplanting in the morning allows seedlings to adapt to their new surroundings during the cooler daytime hours and provides them with a full day of sunlight for acclimation.