Plants can obtain energy. Plants obtain the energy needed to produce food from sunlight. This process is known as photosynthesis. Photosynthesis captures energy from sunlight to make sugars, or we say the sunlight powers photosynthesis by providing the energy needed for plants to convert carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) into glucose and oxygen. This process includes the inputs and outputs of photosynthesis. It occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, where the green pigment chlorophyll absorbs light energy, primarily from the blue and red wavelengths of sunlight.
In essence, the absorbed energy excites electrons in the chlorophyll, initiating a series of light-dependent reactions. These reactions generate energy-rich molecules like ATP and NADPH, which are then used in the Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions) to synthesize glucose from CO₂.
In this post, we’ll learn where plants obtain energy from and how your plants turn sunlight into energy. By the end of the article, we’ll also demonstrate what supplemental lighting you can use when there is no sufficient light.
Table of Contents
Where Do Plants Get Their Energy From?
Plants get their energy primarily from sunlight through the process of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll in the chloroplasts absorbs sunlight, which provides the energy needed to convert carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) into glucose (a form of chemical energy) and oxygen. This glucose is the plant’s main energy source, promoting plant growth, reproduction, and other cellular activities through cellular respiration.
On the other hand, plants can store excess glucose as starch for later use or use it to build structural components like cellulose. While sunlight is the initial energy source driving this process, the stored chemical energy in glucose supports the plant's metabolic functions even in the absence of light.

Where Do Plants Get Their Energy From?
Do Plants Get Energy from Glucose?
Yes, plants get energy from glucose. In the process of photosynthesis, here comes glucose, which serves as a primary energy source for plants, fueling various metabolic activities essential for growth and development. During respiration, plants break down glucose to release chemical energy, which is then used for protein synthesis, cell division, and overall maintenance of cellular functions.
Additionally, glucose can be stored as starch for later use or converted into other compounds like cellulose for building cell walls and fats for energy storage. This versatility allows plants to utilize glucose not only as an immediate energy source but also as a building block for other vital molecules necessary for their survival and reproduction.
How Is the Energy Produced by Sunlight Stored in Plants?
Plants store the energy produced from sunlight in the form of glucose, which is synthesized during photosynthesis. When plants create more glucose than they can immediately use, they convert it into starch - a complex carbohydrate that serves as a long-term energy storage molecule. Starch is insoluble so it can be stored in various plant tissues such as roots, stems, and leaves, which allows plants to retain energy without affecting their osmotic balance.
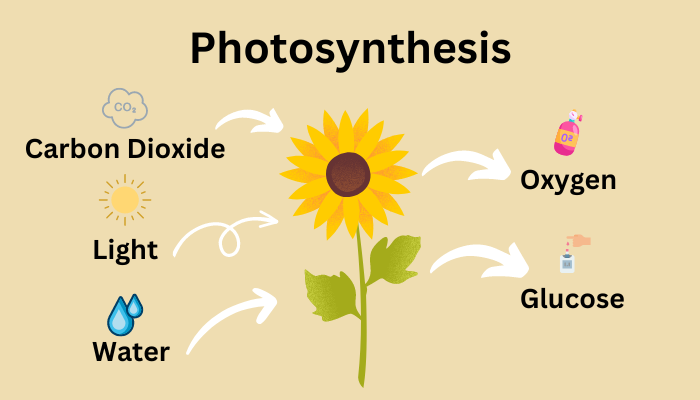
Inputs and Outputs of Photosynthesis
Despite starch, glucose can also be converted into other forms of energy storage like fats and oils, particularly in seeds. This stored energy can later be broken down back into glucose when needed for cellular respiration, providing the plant with the necessary energy for growth and metabolic activities during periods when photosynthesis is not occurring, such as at night or during winter.
What Thing Is Attached to Houses and Absorbs the Sunlight?
The thing attached to houses that absorb sunlight is solar panels. These panels are typically mounted on rooftops and are designed to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through the process of photovoltaics. Solar panels consist of many solar cells made from semiconductor materials, which generate direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
Solar panel mounting systems secure these panels, ensuring they remain stable and effective in capturing solar energy. Various mounting options are available, including roof mounts and ground mounts, which can be tailored to different roof types and orientations for optimal energy production.
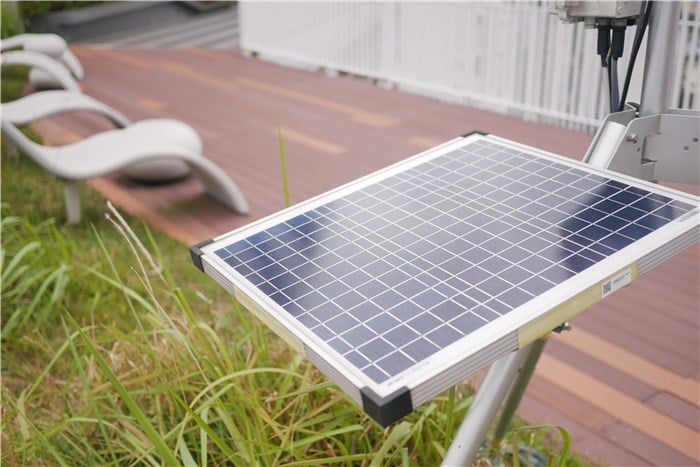

Solar Panel That Attached to Houses and Absorbs the Sunlight
Can LED Lights Mimic Sunlight?
As sunlight plays an important role in photosynthesis, you need to give adequate light to support your plant’s growth. This brings us to the question of whether LED grow lights can 100% replace sunlight.
2025 Newest Version Spider Farmer SF1000D 100W Full Spectrum LED Pflanzenlampe
In stock
2025 Newest Version Spider Farmer SF2000Pro Samsung LM301H EVO LED Pflanzenlampe For 3 Plants
In stock
2025 Newest Version Spider Farmer® SF2000 Samsung LM301H EVO LED Pflanzenlampe For 3 Plants
In stock
2025 Spider Farmer® SF1000 Samsung LM301H EVO LED Pflanzenlampe
In stock
2025 Spider Farmer® SF4000 450W Samsung lm301H EVO LED Grow Light
In stock
2025 Spider Farmer® SF7000 650W Foldable LED Pflanzenlampe
Out of stock
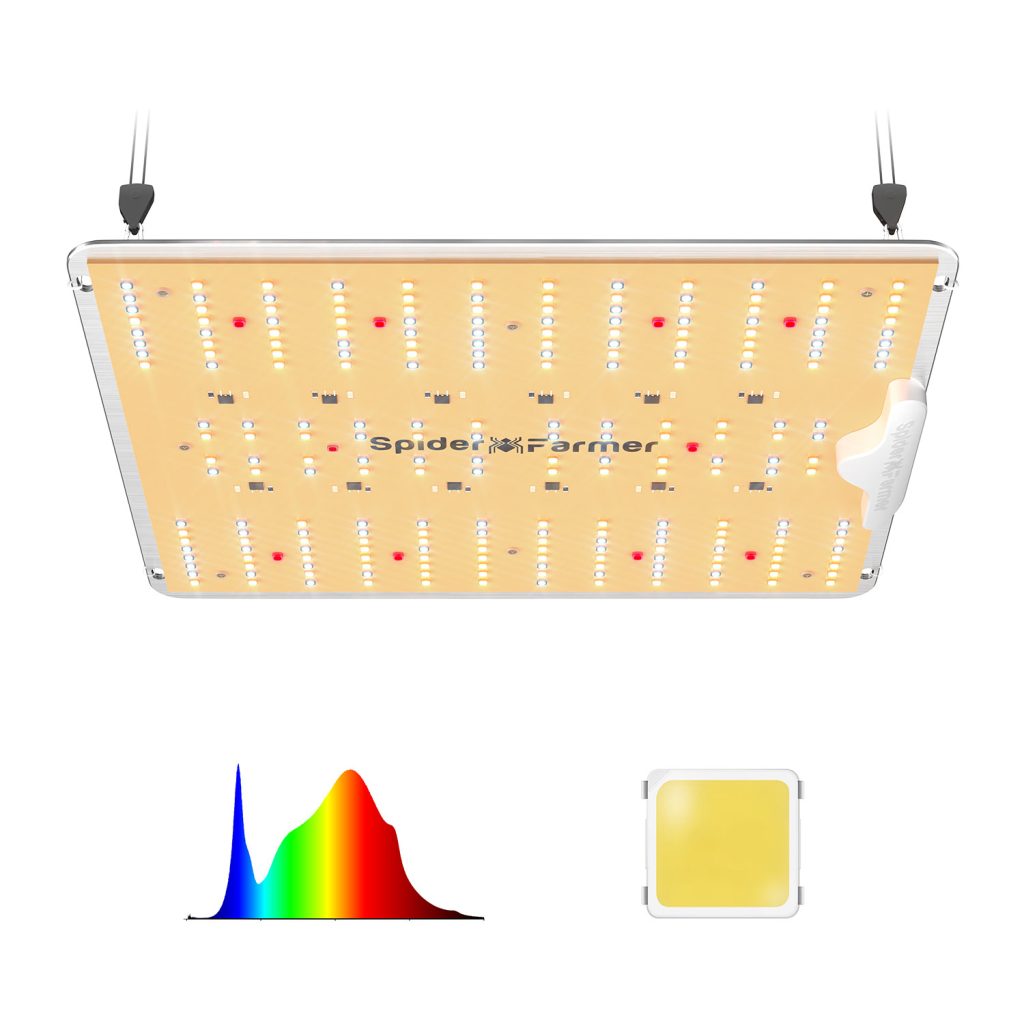
The Spectrum of LED Lights
LED grow lights have developed a lot over the years. Modern LED grow lights can be used to emit specific wavelengths that correspond closely to those found in natural sunlight. For example, full-spectrum LED lights can cover a broad range of wavelengths, providing a balance of blue and red light along with other colors in the spectrum.
- Blue Light (400-500 nm): Essential for vegetative growth, promoting strong stems and leaves.
- Red Light (600-700 nm): Important for flowering and fruiting stages, encouraging blooming and ripening.
Benefits of LED Grow Lights
LED grow light Vs sunlight - Which is better? Here is what LED grow lights can bring to you.
Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume less power compared to traditional grow lights, making them a cost-effective choice for long-term use.
Low Heat Emission: Unlike incandescent or fluorescent lights, LEDs produce less heat, reducing the risk of overheating plants and allowing for closer placement to foliage.
Long Lifespan: LEDs can last up to 50,000 hours, providing consistent light without frequent replacements
Limitations of LED Grow Lights
While LEDs can mimic sunlight to a degree, there are some limitations:
- Full Spectrum Availability: Not all LED grow lights offer a complete spectrum. Some may lack the necessary wavelengths for optimal plant growth.
- Intensity: Natural sunlight varies in intensity throughout the day, and while LEDs can be adjusted, they may not replicate the dramatic shifts in light intensity that plants experience outdoors.
Conclusion
In summary, plants obtain the energy needed to produce food through the process of photosynthesis. This is a remarkable mechanism that turns sunlight into chemical energy. By utilizing chlorophyll, plants capture sunlight and convert carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water from the soil into glucose and oxygen. This glucose serves as a vital source of energy for growth, reproduction, and overall metabolic functions.